"Severe Alteration of the Cell Surface in Acinetobacter baumannii to Unravel Peptidoglycan Physiology"

Dr. Brent Simpson
Bio:
Brent Simpson trained at the Ohio State University, where he received his Ph.D. working in the laboratory of Natacha Ruiz. During his Ph.D., he studied how Gram-negative bacteria build the outer membrane and published three lead-author papers exploring the mechanism of LPS transport. He also received awards for both excellence in teaching and a distinguished dissertation during his graduate work. Brent then moved to the University of Georgia to work with Stephen Trent.
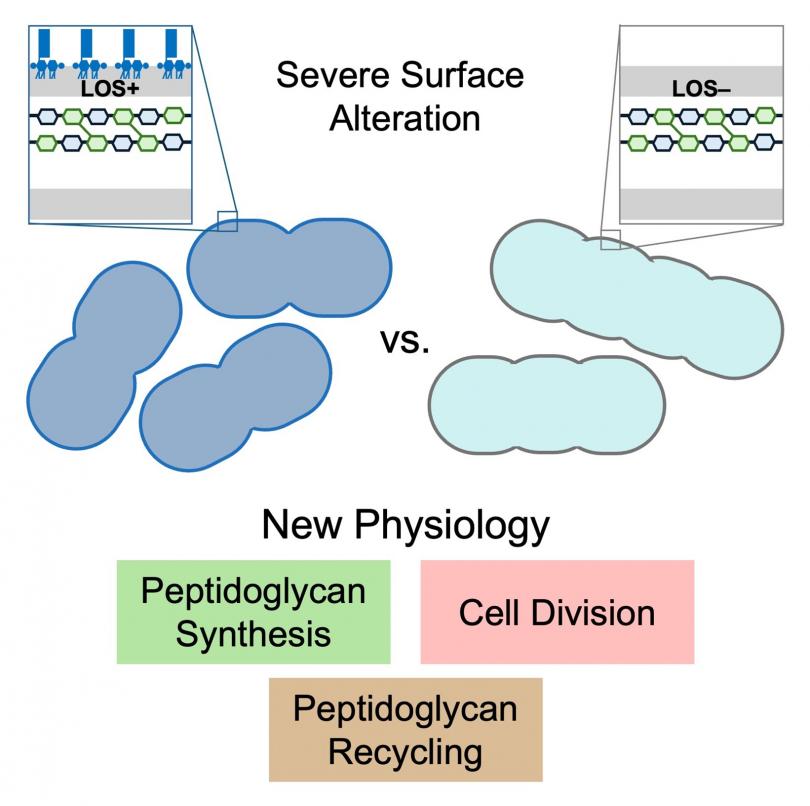
He began working on why LPS is essential in most Gram-negative bacteria using a rare model organism that is able to survive with complete absence of its version of LPS that is missing O-antigen and called LOS. He performed the first transposon-sequencing in a Gram-negative organism completely missing LPS or LOS. This experiment revealed new details about multiple aspects of peptidoglycan physiology in the Gram-negative pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii.
He has published four papers in mBio, PNAS and Journal of Bacteriology following up on peptidoglycan physiology. In addition, he was awarded an NIH F32 Kirschstein fellowship and the UGA Postdoctoral Research Award for his research contributions. He plans to leverage his data set to learn more about cell physiology of Acinetobacter and other Gram negatives with the hope of developing strategies to overcome multi-drug resistant infections. Brent is passionate about microbial physiology, mentoring and teaching students, and his three cats.
Abstract:
Bacteria have evolved different cell envelope compositions that provide them specific advantages in their natural environments or as human pathogens. Gram-negative bacteria have a three-layered cell envelope with an inner membrane, peptidoglycan, and outer membrane.
The outer membrane has asymmetric organization of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or lipooligosaccharide (LOS) only on the cell surface. LPS and LOS differ only in the presence (LPS) or absence (LOS) of an O-antigen. LPS/LOS is essential in most Gram negatives serving both as a permeability barrier and providing rigidity to the cell surface. Peptidoglycan is a mesh of long polysaccharide chains crosslinked with short peptides, that also provides rigidity to the cell. The outer membrane and peptidoglycan are critical structures of the cell that if targeted by antimicrobial therapy can cause bacterial clearance.
The high-priority Gram-negative pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii normally produces an LOS-containing outer membrane, but it is remarkably able to survive even with complete loss of LOS. We have used the comparison of A. baumannii with and without LOS as a critical tool to understand how it builds its cell envelope. A transposon sequencing approach in A. baumannii completely missing LOS unveiled new aspects of peptidoglycan synthesis, recycling, and degradation during cell division. Understanding the biogenesis of the outer membrane and peptidoglycan has broad implications in bacterial pathogenesis, antimicrobial resistance and the development of new therapeutic strategies.

 Dr. Veronika Kivenson
Dr. Veronika Kivenson
 Dr. Brittany Belin
Dr. Brittany Belin Dr. Stefan Katharios-Lanwermeyer
Dr. Stefan Katharios-Lanwermeyer